
With more and more people now preferring to use smartphones over PCs, it often becomes a conundrum for businesses to choose between web apps and native apps to provide users a pleasing experience they always expect from developers.
Native app is meant for a certain mobile device and is installed directly onto the device after downloading it from an online store, like Google Play if the phone is supported by Android and The App Store in case of iOS phones. Web app, on the other hand, is not an app in actual, but a website that pretends to be a native app. It runs inside the phones browser and cannot be downloaded from online stores.

This article aims at adding to your knowledge about seven main differences between web apps and native apps.
-
Speed: Native app is much faster than web app as it takes full advantage of your devices processor power and features, like GPS, camera, notifications etc. Web apps are slow and do not have access to all on-board hardware and software on a mobile device.
-
Platform: To develop a native app, developers need to have specialized skills and need to put a lot of effort as each mobile application development platform is different. For example, Java for Android and Objective-C for iOS. Web apps, on the other hand, are easier to develop and are written in HTML5, CSS3, Javascript etc. The point to note here for developers is that they would need standardized SDKs if going for a native app. SDKs are often provided by the manufacturer of the platform. There is no concept of using SDKs for developing a web app.
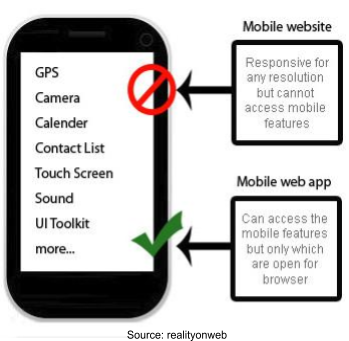
-
Cost: Development cost of native app is much higher compared to web app. The cost of developing a native app further increases if developers are supporting multiple mobile devices. Web apps do not cost much in development as they are accessed through browsers.
-
Updates and maintenance: Updating a cross-platform mobile app is expensive and users are also required to download updates time and again to have the latest version. The cost associated with maintaining a web app is not very high and updates can be easily made as require one central place, so if you have limited budget, you may like to go for a web app.
-
Internet connectivity: All web apps are internet enabled, meaning connectivity is must to access a web app, which is not the case with mobile apps, though you need the internet connectivity the first time when you download it from an online store. Even offline, native apps deliver top-notch performance, with all graphics, images, scripts and data.
-
Visibility and attention: Mobile apps are stored as an icon on the screen of a mobile device, thus easily visible and attract attention of a user. For web apps, a url needs to be entered in the phones browser, which a user can bookmark, but its no hyperbole to say that native apps are far better than web apps when it comes to visibility and attracting attention.
-
Monetization ease: Making money with native apps is also easier as online stores, like Google Play, handle all payment work. With web apps, you need to set up a payment gateway for subscription or membership yourself, which increases a lot of effort on your side.
Please consider all these aspects to make an informed decision before venturing into app business.
1 Comment(s)