Cryptography is based on the calculation and manipulation of data streams and the process to decrypt the data. It will allow you to store the sensitive information and then send it to the network so that the data cannot be read by anyone outsider.
While cryptography is the science of securing data, cryptanalysis is the science of analyzing and breaking secure communication.
Classical cryptanalysis involves the analytical reasoning, application of mathematical tools, pattern finding, patience, determination, and luck. Cryptanalysts are also called intruders.
Conventional cryptography
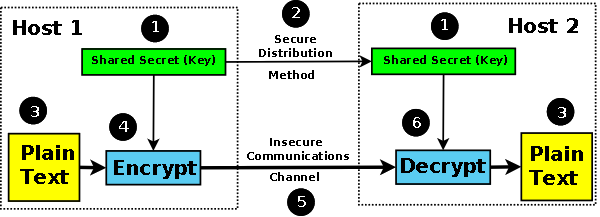
In conventional cryptography, also called secret-key or symmetric-key encryption, one key is used both for encryption and decryption. The Data Encryption Standard (DES) is an example of a conventional cryptosystem that is widely employed by the Federal Government.

Caesar's Cipher
An extremely simple example of conventional cryptography is a substitution cipher. A substitution cipher substitutes one piece of information for another.
This is most frequently done by offsetting letters of the alphabet. Two examples are Captain Midnight's Secret Decoder Ring, which you may have owned when you were a kid, and Julius Caesar's cipher. In both cases, the algorithm is to offset the alphabet and the key is the number of characters to offset it.
For example, if we encode the word "SECRET" using Caesar's key value of 3, we offset the alphabet so that the 3rd letter down (D) begins the alphabet.
So starting with
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ
and sliding everything up by 3, you get
DEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZABC
where D=A, E=B, F=C, and so on.
Using this scheme, the plaintext, "SECRET" encrypts as "VHFUHW." To allow someone else to read the ciphertext, you tell them that the key is 3.
0 Comment(s)